PCOS is very common in one in five women in India now. Many of them do not know the symptoms of PCOS. They deal with it differently. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects women causes various problems such as weight gain, hormonal imbalance, irregular cycles, unwanted hair growth, acne, painful cramps, etc. commonly, women got to know they have PCOS when they have trouble getting pregnant, but it often begins after the first menstrual period, at the age of 11 or 12. It can also develop in the 20s or 30s. Women during their childbearing years. It involves cysts in the ovaries, high levels of male hormones, and irregular periods.
Symptoms
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual periods are common.
- Excess Androgen Levels: Elevated levels of male hormones can lead to physical signs such as excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), severe acne, and male-pattern baldness.
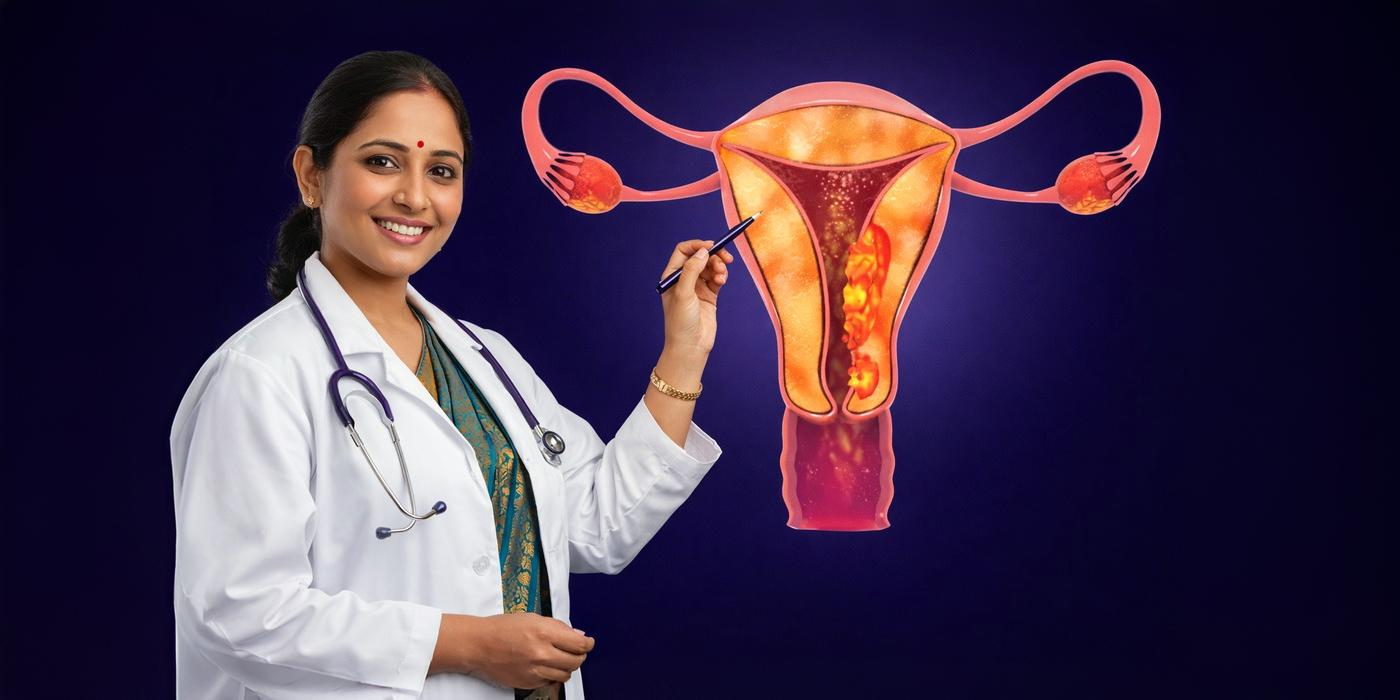
- Polycystic Ovaries: The ovaries may become enlarged and contain numerous small cysts.
Causes
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetics: PCOS tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
- Insulin Resistance: Many individuals with PCOS have insulin resistance, which can lead to elevated insulin levels and increased androgen production.
- Inflammation: Low-grade inflammation is often present, which can stimulate polycystic ovaries to produce androgens.
Complications
PCOS can lead to several health complications, including:
- Infertility: PCOS is one of the most common causes of female infertility.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Increased risk of high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, which are risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance associated with PCOS increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Endometrial Cancer: Irregular menstrual cycles can increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: A detailed medical history and symptom review.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs of excess hair growth, insulin resistance, and acne.
- Blood Tests: Measuring hormone levels, including androgens and insulin.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: Visualizing the ovaries and the presence of cysts.
Treatment
While there is no cure for PCOS, various treatments can manage symptoms:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, a healthy diet, and regular exercise can help manage symptoms and improve insulin resistance.
- Medications:
- Hormonal Birth Control: Regulates menstrual cycles, reduces androgen levels, and improves acne.
- Metformin: Improves insulin resistance and lowers insulin levels.
- Anti-Androgen Medications: Reduces hair growth and acne.
- Fertility Treatments: For those trying to conceive, medications like clomiphene citrate can induce ovulation.
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you have skipped periods, or if you have other PCOS symptoms like hair growth on your face or body, weight gain, acne, etc. Also, talk to a doctor if you’ve been trying to get pregnant for a year or more without success. Doctors typically diagnose PCOS in women who have at least two of these three symptoms:
- high androgen levels
- irregular menstrual cycles
- cysts in the ovaries
Treatment plan
If you have PCOS and you’re obese, losing weight and eating a healthy, balanced diet can make some symptoms better. Generally, women need a combination of lifestyle changes and medications to treat PCOS. Your doctor will create a treatment plan for you tailored to treat your symptoms. The purpose of PCOS treatment is to control symptoms. If you are preparing for conception and medication and lifestyle changes do not fulfill the purpose then there are some additional treatments are to be perform.
- Surgery: A procedure called ovarian laparoscopy might make your ovaries work better when ovulation medications don’t. The doctor makes a small cut in your belly and uses a tool called a laparoscope with a needle to poke your ovary and wreck a small part of it. The procedure changes your hormone levels and may make it easier for you to ovulate.
- In vitro fertilization or IVF: With this procedure, your egg is fertilized outside of your body and then placed back inside your uterus. This is considered as the best way to get pregnant when you have PCOS, but it can be expensive.
If you’re concerned about your PCOS and don’t already have a gynecologist, you can visit the Best Gynaecologist in Faridabad. The specialist at the Best IVF Centre in Faridabad helps restore hormonal balance, reduces cyst formation, gets a natural period on time every month, and boosts fertility.